The Common Vein Copyright 2012
Aortic Dissections
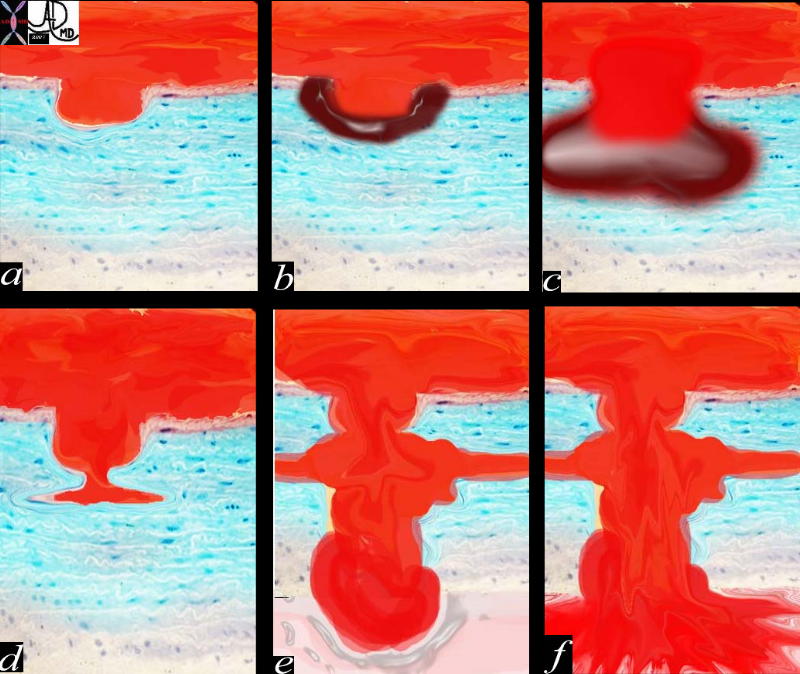
The Pathogenesis of Aortic Wall Dissection |
|
aorta artery atherosclerosis atheroma acute aortic syndrome a aortic ulcer b = acute mural hematoma c = acute mural hematoma large d = focal dissection e penetrating ulcer f rupture histology histopathology Davidoff art pathogenesis Copyright 2012 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 42409c01.800 |
Dissection of the Ascending Aorta
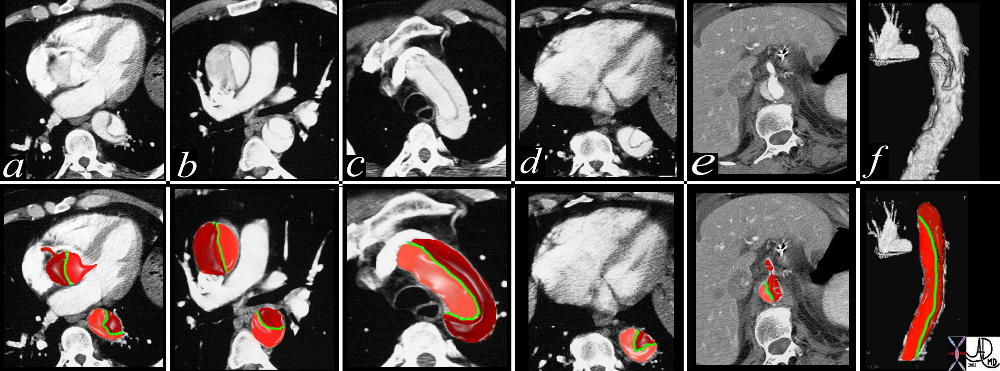
Type A Aortic Dissection |
|
This combination of images from a CTscan through the thorax, reveals an aortic dissection starting at the level of the aortic valve and extending into the abdomen with involvement of the celiac axis. The true lumen is overlaid in pink while the false lumen is over;laid in a darker red. The green structure is the intimal flap. Flow in the false lumen is slightly delayed and slower as seen by the lower density of the contrasyt within it. Copyright 2012 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. 19412c02 code CVS artery AO aorta dissection fx crescent |
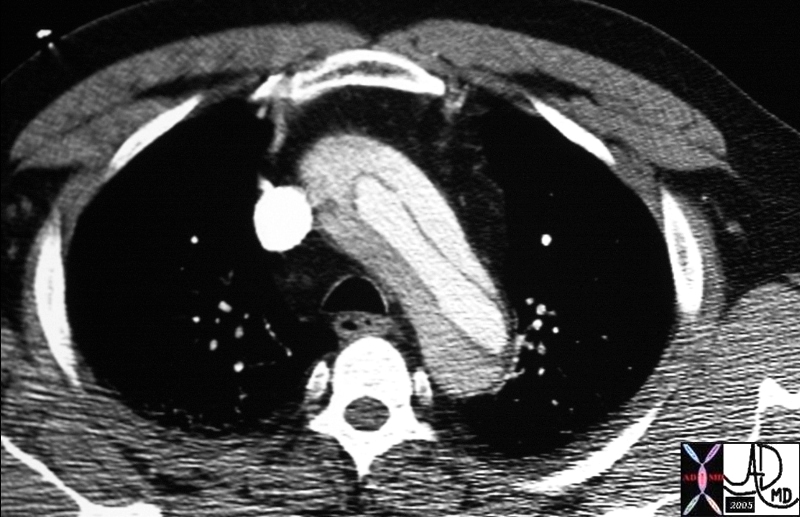
Arch Dissection – Narrowed True Lumen |
|
thorax thoracic aorta arch aorta fx dissection dx aortic dissection type A CTscan Copyright 2012 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 20449 |
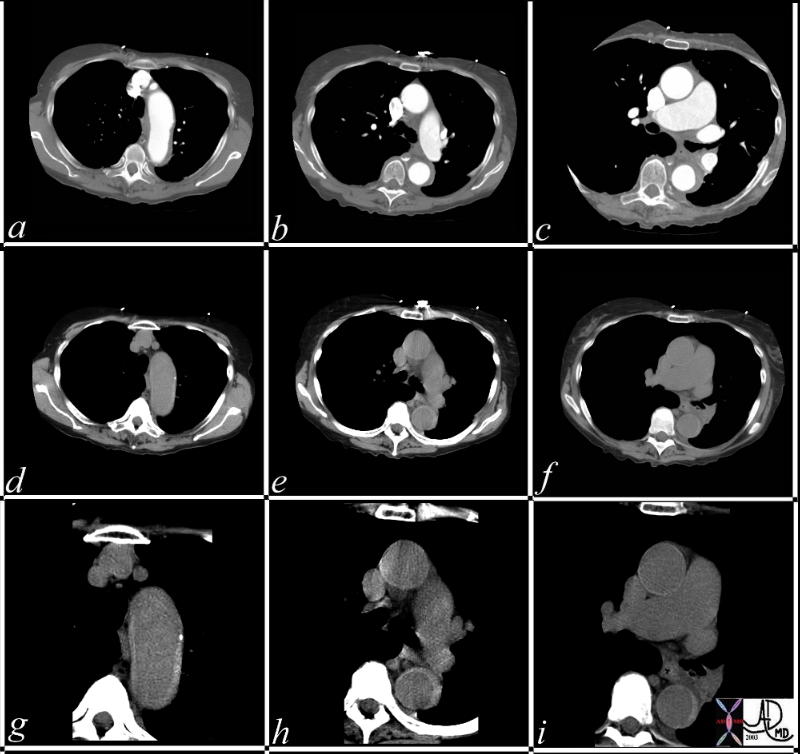
36865c |
| This series of CT scans were taken 1 day apart. The patient presented with chest pain and the soft tissue changes around contrast filled aorta (a,b,c) suggested a chronic dissection, or an acute thrombosed dissection. 1 day later the non-contrast CT clearly reveals an acute thrombosed dissection (d,e,f) that started in the arch and extended along the descending thoracic aorta. The last series (g,h,i) enhance the non contrats study. A non contrast CT followed by contrast injection, is an important tchnique to optimally characterise acute changes in this clincal setting.
Copyright 2012 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 36865c |
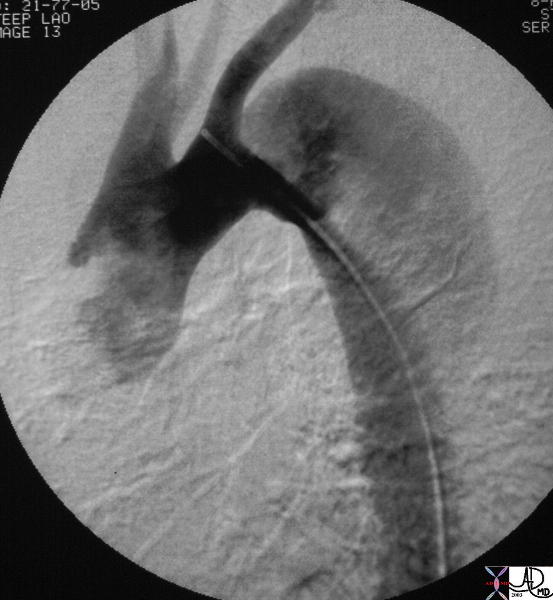
Descending Thoracic Aortic Dissection |
|
The digital angiogram in the LAO projection shows an intimal dissection starting just after the left subclavian artery. The true lumen is medial and smaller than the laterally and leftward placed larger false lumen. 35204 Courtesy Laura Feldman MD. code CVS artery aorta thorax thoracic descending dissection angiogram code aorta artery dissection flap. Courtesy of Laura Feldman MD. 35204 |
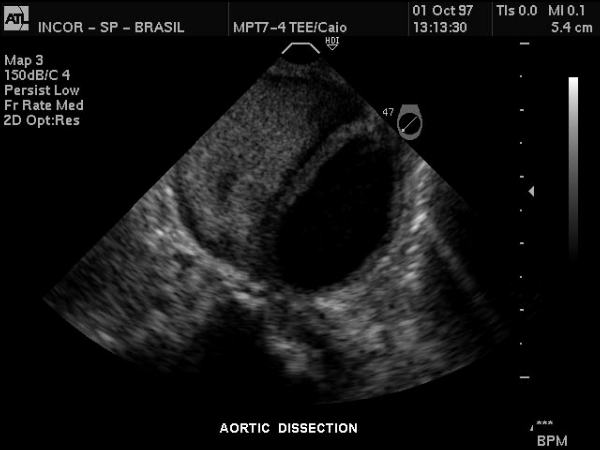
Thoracic Aorta – Dissection |
|
Gray scale US of the descending thoracic aorta showing a hypoechoic true lumen (black) and homogeneous echoes of the thrombosed lumen in this patient with aortic dissection. Courtesy Philips Medical Systems 33167 |
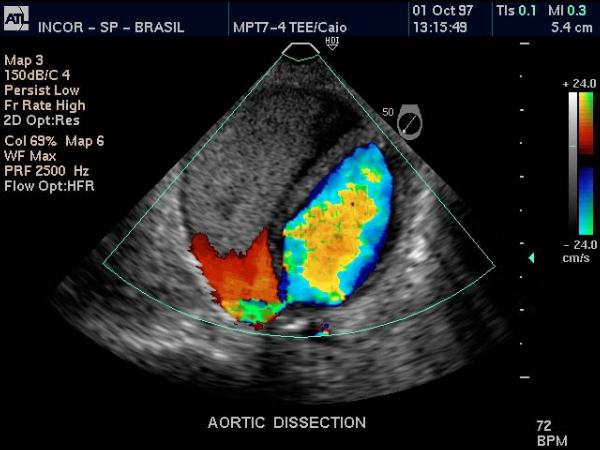
Color Flow Doppler – Descending Thoracic Aorta Dissection |
|
Doppler US of the descending thoracic aorta showing flow in the true lumen (color) and no flow in the thrombosed lumen (gray echoes) in this patient with aortic dissection. Courtesy Philips Medical Systems 33166 |
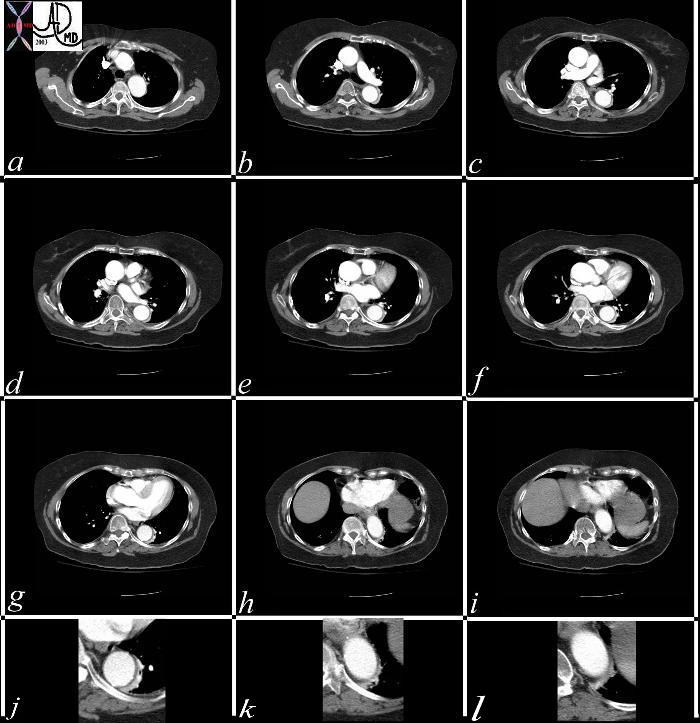
Atelectasis Masquerading as a Dissection |
|
This series of CT scans from the arch to the abdominal inlet shows a curvilinear density around the aorta on its left lateral edge that masquerades as a dissection The last three images (g,h,i) and their magnified counterparts below them (j,k,l) shows air bronchograms opacified vessels within the crescentic density, and deviation from the contour of the aorta, confirming the atelectatic nature of the crescent. Copyright 2012 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 37071c |
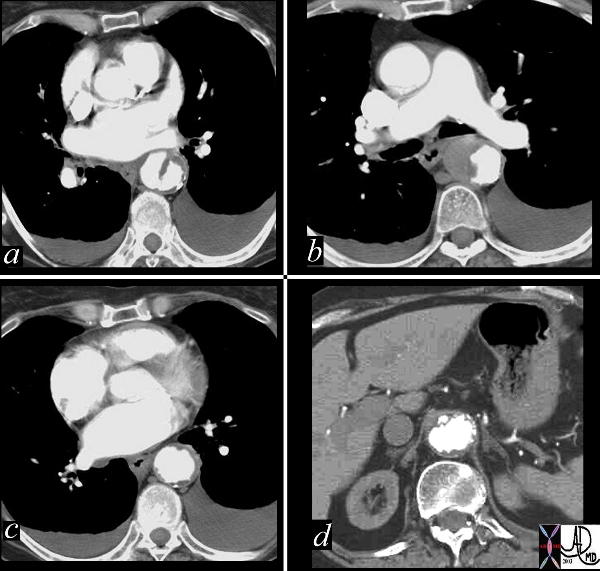
Dissection Caused by Ulcerating Plaque Complicated by Mural Hematoma |
|
This combination of images reflects the CTscan of a patient who presented with acute chest pain, and has findings reflecting a focal dissection of an atheromatous aorta. Note in (a) how thick the “intimal” flap is. Note also the mural dissection or hematoma with no flow within it. (b) Other parts of the descending aorta (c) and abdominal aorta (d) show only severe atheromatous disease. Copyright 2012 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. 19416c |
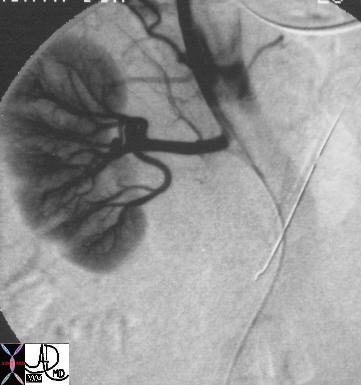
True Lumen Compressed and Supplying Right Renal Artery |
|
artery aorta fx dissection dx dissection angiography Copyright 2012 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 17474 |
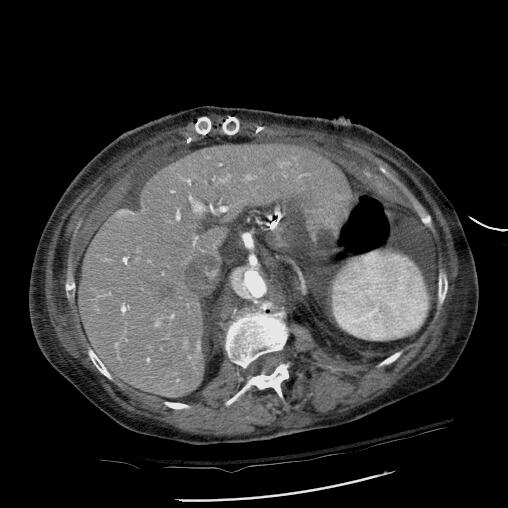
True Lumen Compressed on Left Slow Flow in False Lumen |
|
abdomen artery + abdominal aorta + fx crescentic crescent shaped false lumen fx dissection + dx iatrogenic + imaging radiology CTscan radiologists and detectives Copyright 2012 Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD 19408 |
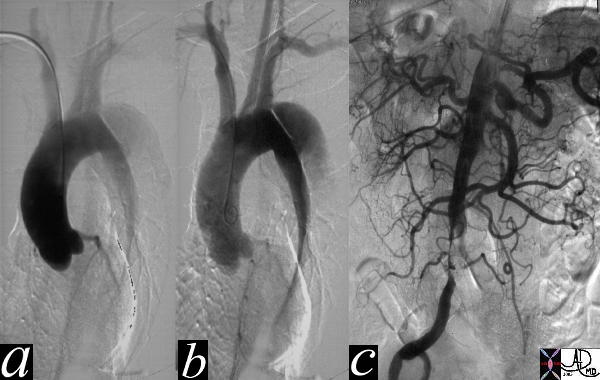
Type B Dissection |
|
The thoracic angiogram reveals an aortic dissection which starts just after the left subclaian artery. The true lumen is the narrowed medial lumen which is denser than the larger lateral false lumen. (a,b) In (c) the A-P view reveals a patent proximal abdominal aorta, but the distal narrowing and occlusion of the the left iliac artery suggests that the dissection has progressed distally. In the image 35124c the cross sectional images of the abdominal aorta reveal that the true lumen of the distal aorta is in fact quite narrowed. Courtesy Laura Feldman MD. 35116c |
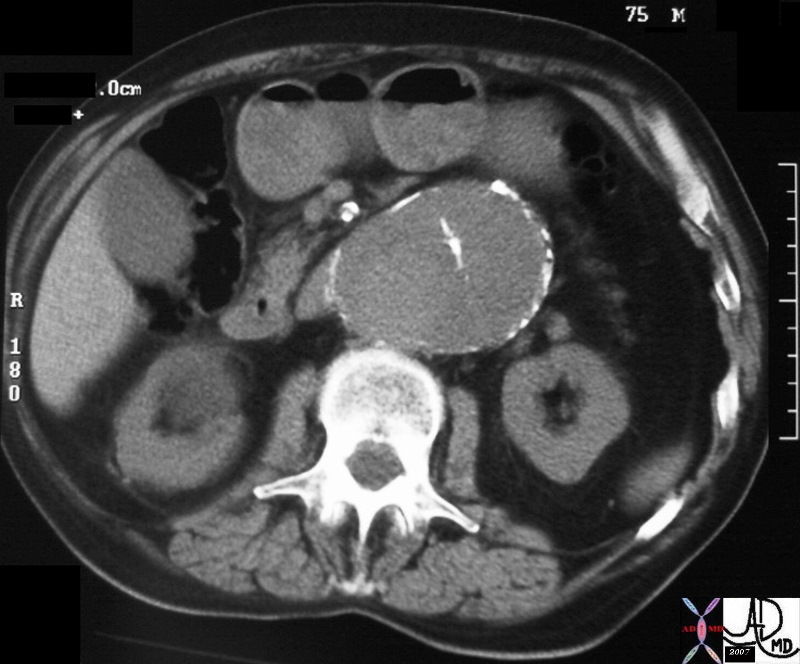
Chronic Aortic Dissection |
|
hx 75 male with abdominal pain abdomren abdominal AAA aneurysm fx mural calcification thrombosed aortic dissection chronic dissection CTscan Copyright 2012 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 31262 |
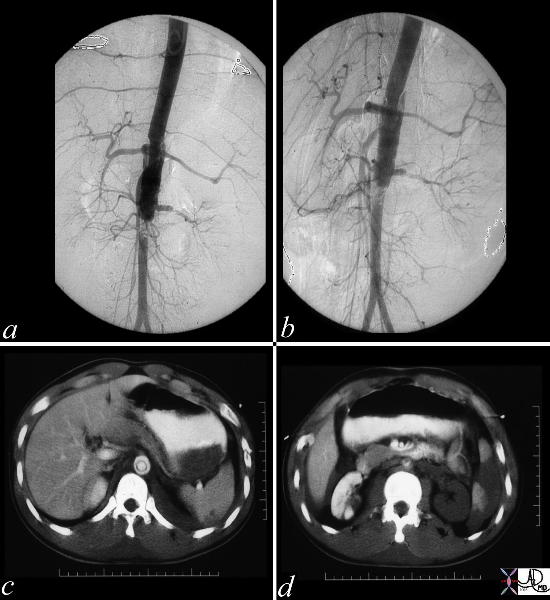
Acute Traumatic Dissection |
|
These images represent a traumatic dissection of the abdominal aorta caused by a compression injury to the abdomen. The angiograms in a and b shows what appears to be a complex tear of the aorta with a dissection and then a subtotal obstruction of the aorta distally. The CTscan shows (c) thedissection to better effect, with a subtotal narrowing of the aorta distally. Not also the injury of the left renal artery on the angiogram as well as the lack of perfusion of the left kidney on the CT scan. Copyright 2012 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. 14734c |
Clinical
The clinical presentation is usually dramatic with hyperacute “shearing” or “ripping “chest or back pain. Proximal Anterior chest pain is usually associated with tears of the ascending aorta, while dissection of the descending aorta usually gives interscapular pain. Most patients are hypertensive. Findings on examination include aortic insufficiency (50%), pulse deficits (50% – commonly involve the brachiocephalic vessels) or neurologic manifestations Distal dissections may reveal pulse deficits of the left subclavian or femoral vessels
Diagnostic Tools
The radiologic diagnosis is often suspected on the plain film with the widened mediastinum and more specifically a blunted aortic knob or thickening of the wall of the knob more than 5 mm past the calcified aortic intima (Ring sign). CT, MRI and trans-esophageal echocardiography are all used with high sensitivity and specificity. TEE sensitivity/specificity of 99/98% Aortic angiography is an invasive procedure but may be best at delineating the extent of dissection
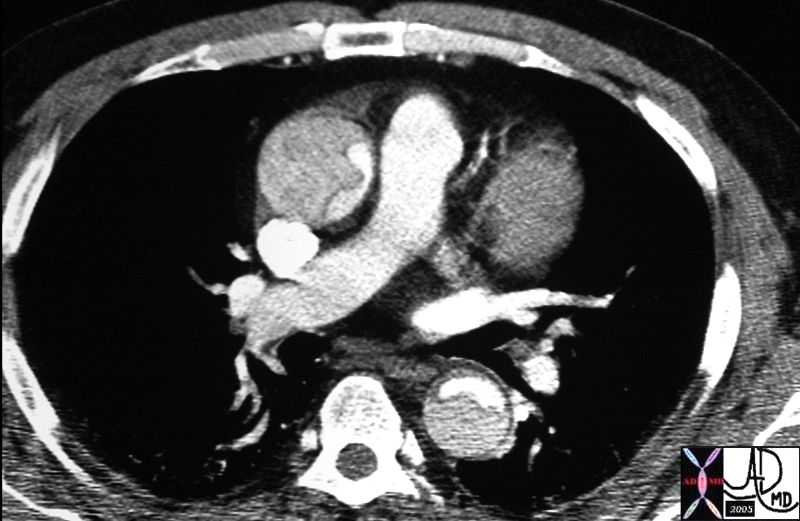
Dissection Involving the Ascending and Descending Aorta |
|
descending aorta ascending aorta fx dissection fx crescent dx aortic dissection type A CTscan Copyright 2012 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 20448 |
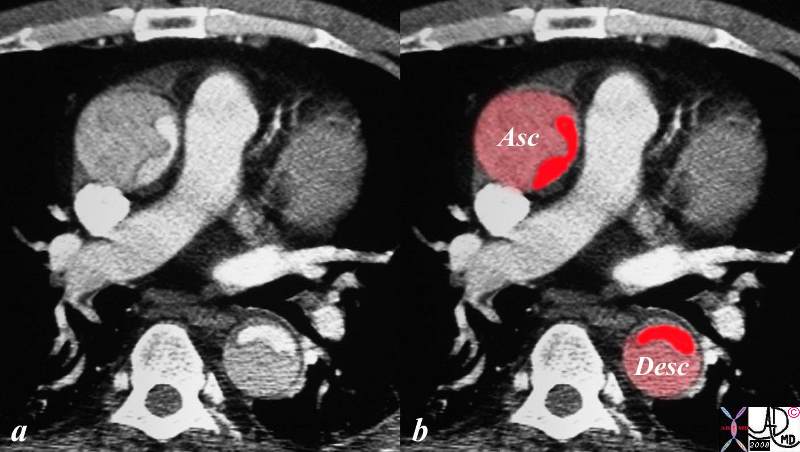
Dissection Involving the Ascending and Descending Aorta |
|
The CT image shows a dissection in the ascending aorta. The lumen consists of the smaller true lumen (with white contrast) and the false lumen (larger with grayer density) The patient presented with classsical sever chest pain that radiated to the back. The involvement of the ascending aorta make s it a type A dissection and therefore treatment requires surgical repair. In this patient however the dissection extended to the descending aorta as well. Either way a type A dissection requires surgery. Copyright 2012 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 20448c03.8s |
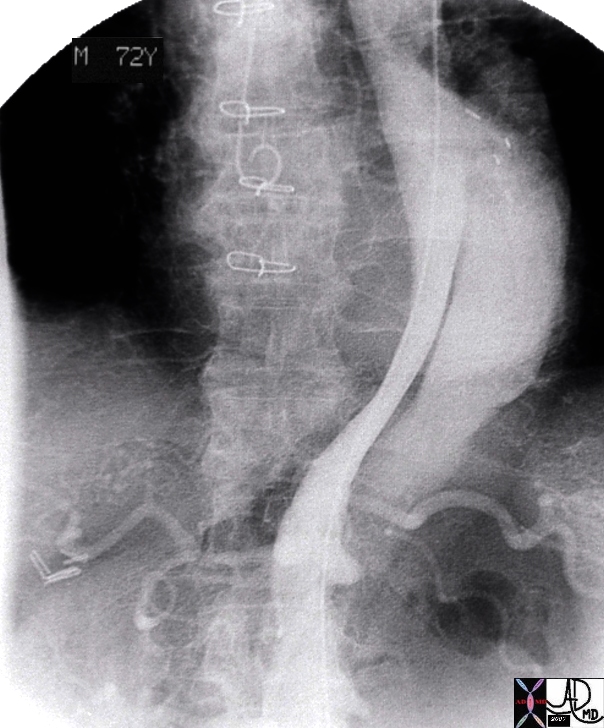
Type B dissection involving descending thoracic and abdominal aorta |
|
thorax abdomen fx dissection true lumen false lumen occluded renal artery angiogram angiography Copyright 2012 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 24588b01 |
Hepatic Artery Dissection
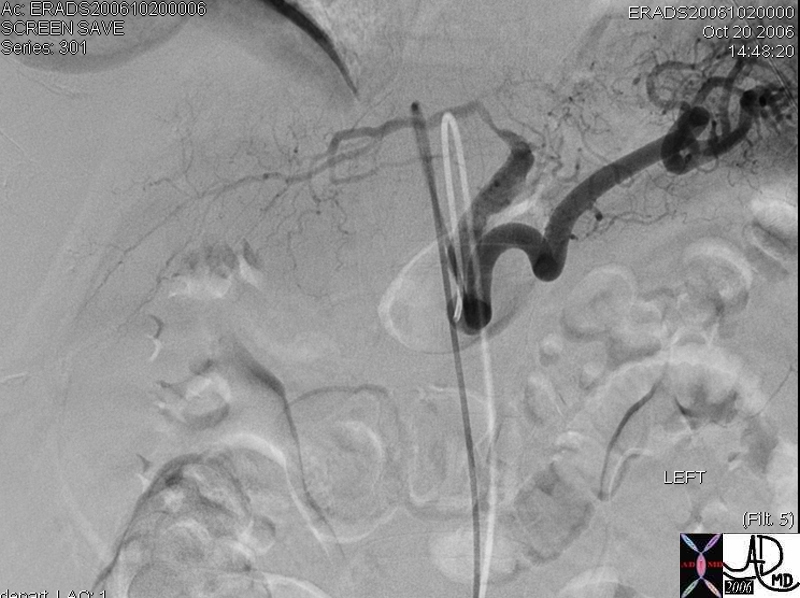
Spontaneous Dissection and Rupture of the Hepatic Artery |
|
50 year old male presents with abdominal pain to the ER liver left hepatic artery fx focal aneurysmal dilatation of the proximal left hepatic artery fx focal narrowing of the mid portion at site of dissection dx spontaneous dissection of the left hepatic artey complicated by intraperitoneal rupture., treated by coil embolisation The common and right hepatic artery arose from the SMA Copyright 2012 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 45278b |
